Some questions for the curious mind
Learning is always fun, at least it's meant to be! If one is interested in looking around and figuring out the science and math behind things, it could provide an endless stream of fun and new learnings. So, here is an attempt to pick the curiousity of your mind! Read on...
Legend:
P: Phenomenon; U:Usage of something we learnt; C: Concept
Question: Why doesn't a spinning coin fall?
Answer: It's so busy going around itself that it has no time to fall :-)
But seriously, the force/energy that you give to the coin when you spin it, if it's strong enough, will put it into spin. But after a while, due to friction with the surface it's spnning on and the air resistance, it will slowly lose its momentum and finally the gravity of earth will pull it down. Till then it will keep spinning!
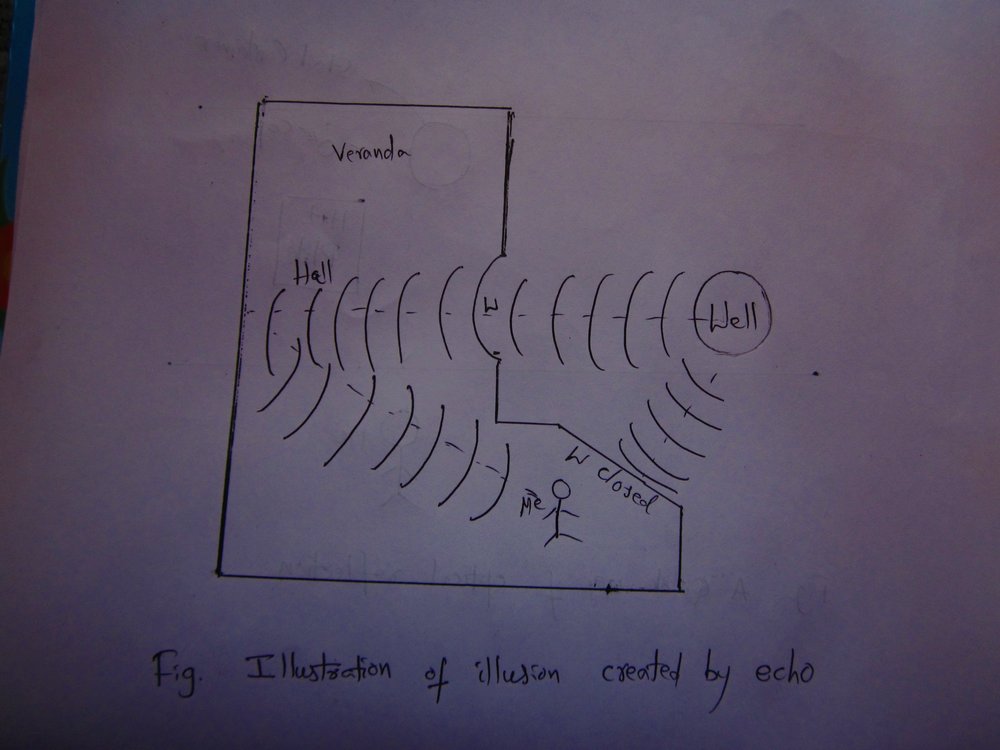
P:The beautiful illustration of sound echo that creates an illusion
The sound of the rain water falling into the well in our portico appeared to be coming from the hall rather than the kitchen because of because the hall window was open and the kitchen diagonal window was closed.
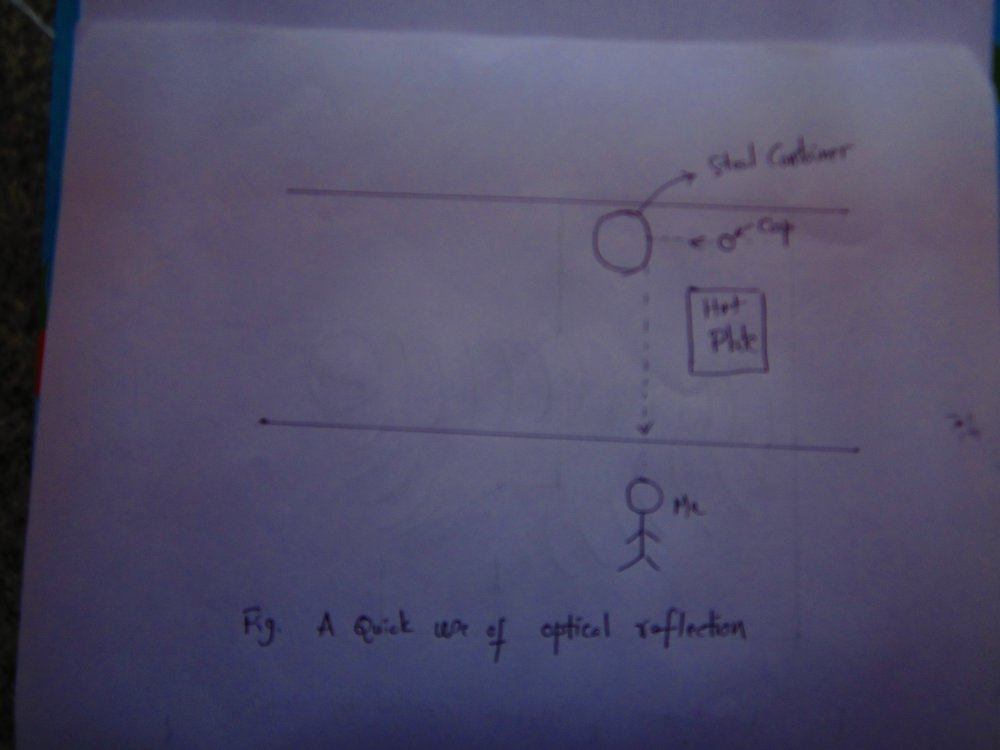
U: A quick use of the phenomenon of optical reflection:
How I found the cap of the milk bottle that fell behind the electric hot plate but was reflected in the steel container that was in my line of vision.
Question: Gas stove versus electric hot plate: When you heat up some water in a steel vessel on a gas stove, the vessel gets too hot to touch. But when you do the same thing on an electric hot plate (aka induction heater) the vessel (rim and side) remain cool enough to hold with bare hands. Why?
Answer:The flame of the gas stove, even in SIM, envelopes the sides of the vessel and steel being a good conductor, heats up quickly whereas the water within it takes time to heat up.
On a hot plate, the source of heat is through high frequency pulses aimed at the center point and it directly gets through to the water through the bottom. The sides of the vessel never receive any direct heat.
Why does dust from the road raise in the wake of a speeding vehicle, especially a four wheeler?
Answer: All the dust particles have suddenly become fans of you, driving that vehicle, and want to follow you!
But seriously, it's because of the vaccum that is created due to sudden displacement of the vehicle in the direction it's going in. When such a vaccum is created, all free things around rush into that vaccum, In this case, all dust particles on the ground rush into that vaccum and go high up in the air. aftre a few seconds, there is no vaccum and so they gradually settle down where they originally were: ground.
Question: When there is hot water in a wide-rimmed vessel, you will be able to hold it by the rim and carry it. How is that? And can you think of a widely seen usage of this phenomenon in any modern machinery?
Answer: The heat conducts from the hot water to the sides of the metal vessel and then up to the rim and quickly dissipates through the side surface area of the rim and so it will be much cooler than the sides that are in constant touch with the hot water inside.
A very effective use of this traditional knowledge is in the use of fins of an air-cooled engine of a motor bike - the heat from the engine is quickly dissipated through the fins.
Question: To open/close a door, push it a) closer to the hinge b) push it closer to the edge. Which one takes less effort?
Answer:
For smaller children: Do you see that if you push it closer to the edge, it takes less effort? Yes! In a way, you are using the door's own weight to do the job.
For older children (high school): The hinge is the fulcrum and so if you push the door at a point closer to the edge, the arm of the couple is longer and so it takes less force/effort.
Question: How can you look at the bright sun (not sunrise/sunset) without any special glasses and without damaging your eyes?
Answer:
Caution: this is only for older children, under elders' supervision.
Interlock the fingers of your hands and leave just a small diamond-shaped gap between any two sets of fingers and look at the sun through that small aperture. You will see it at a much less level of brightness because you are letting a small fraction of the sunlight to hit your eyes and so you can comfortably look at the sun and after a few seconds, your eyes will get adjusted to it and you can even clearly see the solar disk. You can see rainbow colours around the inner edges of those two sets of your fingers due to a phenomenon called diffraction (bending of light around edges).
Question: When you cut bhendi/okra with a kitchen knife, it becomes very sticky with the silky, sticky substance of that vegetable (which is very good for health). But how do you get rid of it from the knife?
Answer: Once I was cutting tomatoes after cutting bhendi/okra. After that, I was surprised to notice that most of the sticky stuff went off the knife. Why?
The sticky stuff from bhendi/okra is mildly alkaline and tomato is acidic (native tomatoes, not the hybrid ones). So, when the two come together, they neutralize each other and so the sticky substance dissolves in the acidic juice of tomato.
Question: Why do sprouts (of whole pulses such as green gram) have, according to scientists, 30-40% more proteins than unsprouted ones?
Answer: When a seed starts sprouting, it's germinating and coming into life from dormant state. At that time, the sprouting plant needs extra proteins. So, the seed, catalysed by the water/moisture converts the non-protein food (at least some of it) in the seed into protein to support the upcoming plant. Hence, the extra 30-40% more proteins in the sprouts.
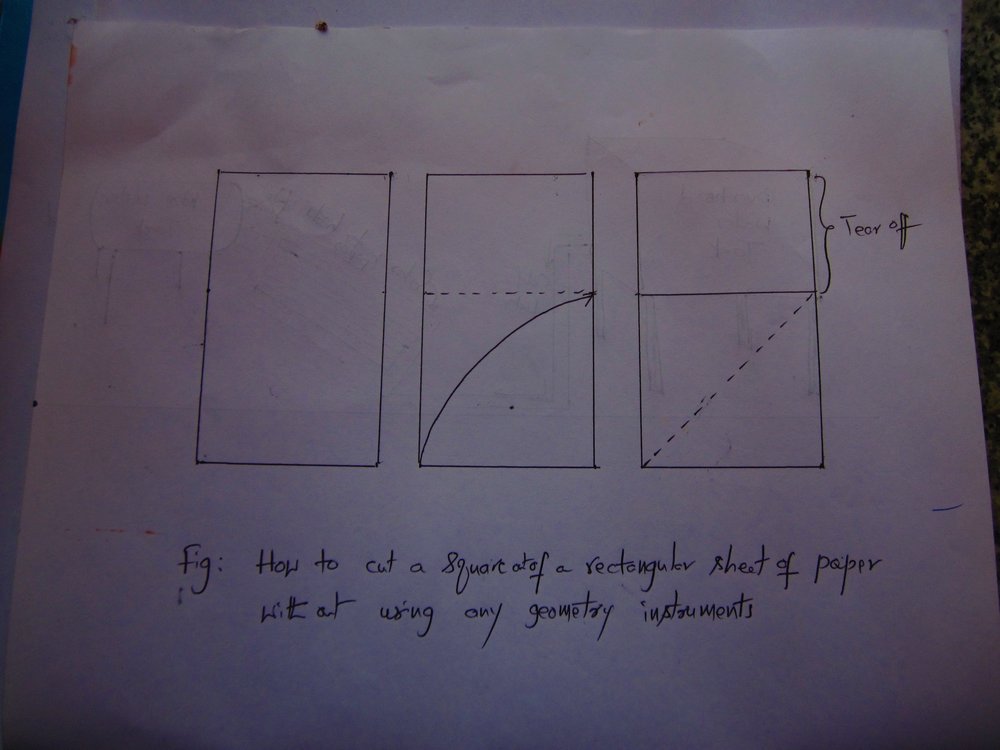
Question: This is a fun question. How do you cut a square out of a rectangular piece of paper?
Answer: Simple. Just hold the 'width' side of the rectangular paper and fold it diagonally onto the adjacent 'length' side of it - so that leaves the extra width of the length uncovered. Tear it off. The you have a square sheet. No geometry instruments needed!
Q: What is the science behind sprinkling cowdung water in front of traditional houses (with non-concretized open space)?
A: It's the bacteria-killing effect of cowdung - when people of the house or the guests walk in - either barefoot or with footwear - over the cowdung-water-sprinkled porch, the bacteria in their feet (or the footwear) get killed or eliminated, thus keeping the house hygienic. Same with mud-floors inside, that are caked with thick paste of cowdung - traditional 'poor' people's houses.
O: Prime numbers in nature
A: Some such prime numbers:
- 5: basic elements (air, water, earth, fire and sky). Of course this is as per humans' classification
- 5: senses
- 5: number of seed cells in a cross-section of okra/bhendi
- Number of petals in a lotus flower is a prime number. Same with many other flowers too.
C: Centre of gravity - the imaginary point in a solid body where its entire mass seems to be concentrated. Here are some fun applications of it.
It could be some small fun demos such as balancing a scale or a long stick on a finger, or lifting a chair with a couple of fingers to walking on a tight rope with a 'balancing' stick in ones hands.
Q: Want iron filings for some fun experiments?
A: No problem! Get a magnet and some mud from your backyard. Run the magnet through the mud - you will find lots of iron filings stuck to the magnet when you take it out! These iron filings occur naturally in earth's soil.
Of course you need to have access to mud. In the urban setup of today, it may be difficult for you, with every visible square foot of open earth covered with concrete or tar/asphalt. In that case, you need to 'buy' mud.
Q: How can you find the height of a tall (and straight) tree or building?
A: Use simple geometry principle of similar triangles. You can do the following on a sunny day if you can get a clear shadow of the tree/building.
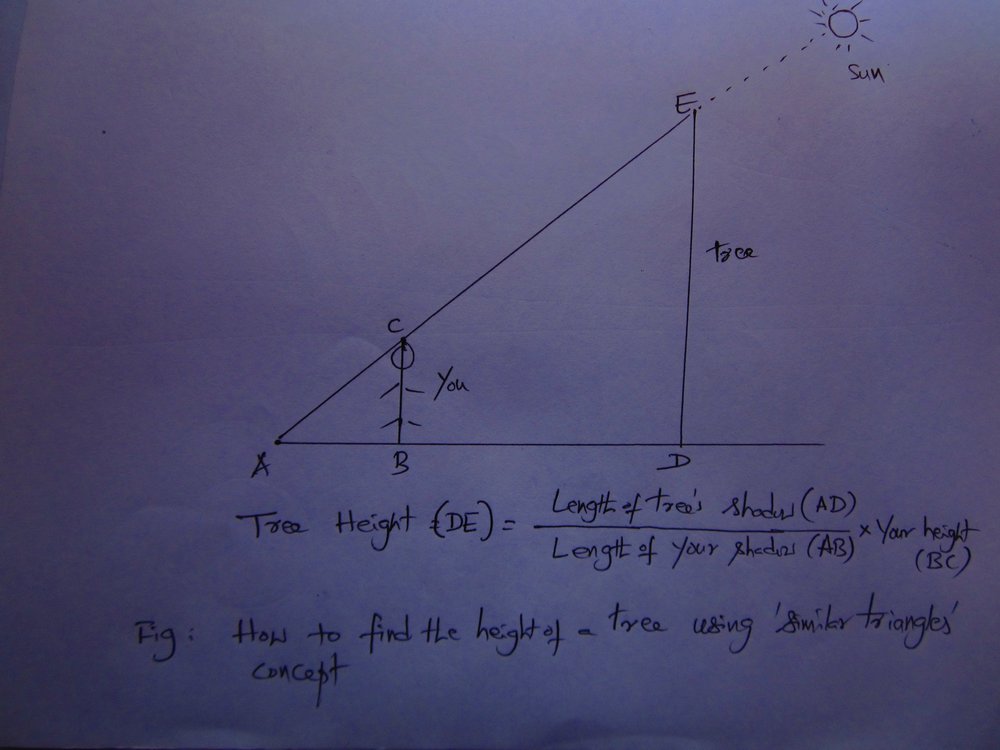
AB/BC = AD/DE
So, DE = (AD/AB) * BC
Tree height (DE) = (Length of tree/building's shadow (AD) / Length of your shadow (AB)) * Your height (BC)
O/Q: Why don't fishes have eyelids, whereas all land animanls, including humans, have eyelids?
A: Many possible reasons. My theory is that on land, through air things move much faster than in water and so to protect their eyes from fast-moving objects or particles, land animals developed eyelids. Also, land animanls seem to have a need to block their eyes from light while sleeping, hence the eyelids.
On the other hand, in water things move much slower, so no fast-moving misslies come to hit the eyes of the fish.
U: Uses of the concept of relative velocity/speed
Answer:
All children: Did you notice, when you are in/on a vehicle on the road, the distance between your vehicle and the one ahead of you? Does it remain the same, increase or decrease?
Mid/high school children: Relative velocity (speed) is the difference between the velocities of two objects moving in the same direction, in this case, your vehicle and the one ahead of you. If the distance remains the same (as your eye measures it), then both are moving at the same speed/velocity. If the distance is reducing, then yours is faster and probably you should slow down, to avoid collision. If the distance is increasing, then the vehicle ahead is moving faster than yours.
Note: Speed is a scalar quantity, with just magnitude and velocity is a vector, with magnitude and direction. But for simplicity sake, I used both terms interchangeably in the above answer.
Q: Why does hot water, when kept in an open vessel, cools down much faster than when the vessel is closed?
A: The answer is rather obvious, but to make it thorough, here it is:
For high-school children: Heat loss happens through conduction, convection and radiation. When the vessel is closed, heat loss (and hence the cooling of the water) happens through the walls and lid of the vessel due to convection and to some/little extent, through conduction, as air is a poor heat conductor.
But when the vessel is open, heat loss is manifold in the form of mass transfer - water vapour carries away much more heat with it than what goes out through conduction and convection.
Q: You open one door and the other door closes / or vice versa! How???
A: Try this with kitchen cabinet doors (double doors). Keep one door slightly open and suddenly pull open the other door. The first door that was slightly open pulls itself shut!
When you suddenly pull open one door, the air just behind it gets pulled out and so there is a sudden vaccum created. So, that pulls the other door in.
When you suddenly close one door, the opposite happens. Air suddenly gets pushed in, and that in turn pushes the other door and that suddenly opens up.
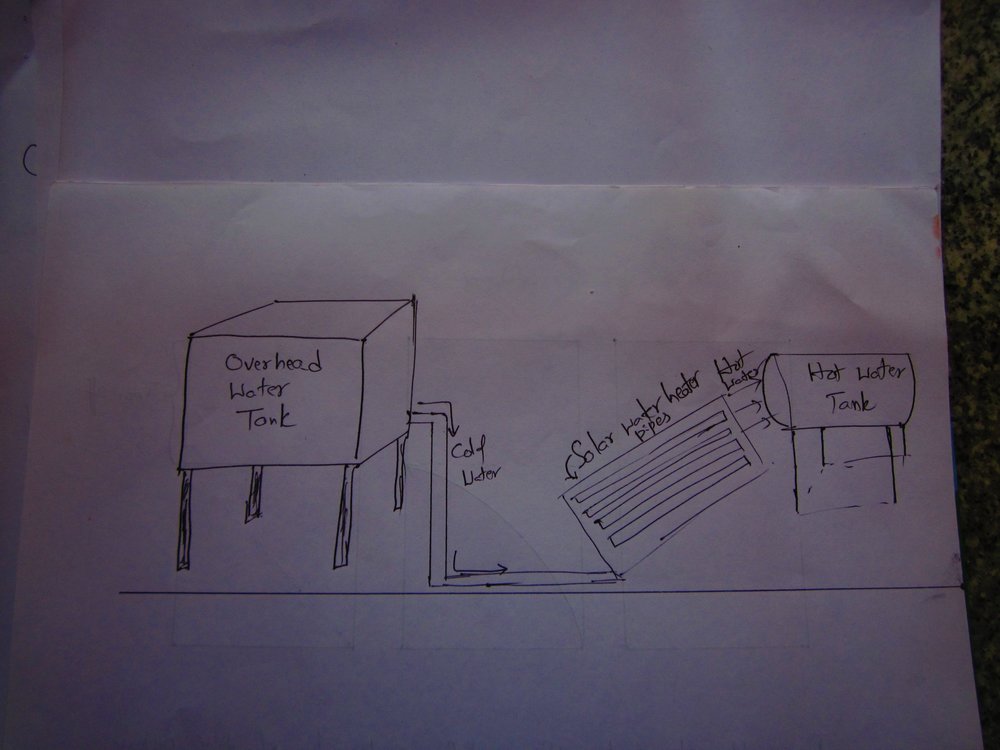
Q: When your bathroom hotwater tap, connected to your solar water heater, goes dry and you pump water from the sump to the overhead tank, which feeds water to the solar water heater, how does hot water starts flowing from the hot water tap?
A: Simple. The hot water tap goes dry when the hot water level in the solar hot water tank goes below the outlet level (see diagram below).
When the overhead tank starts filling, cold water flows into the heating panel tubes and the hot water in those tubes, being lighter than cold water, moves up into the solar hot water tank and starts flowing to the hot water tap in your bathroom.
Q: Take a glass of water. Add a spoon of salt or sugar to it. It melts and disappears. But the water level doesn't increase. By contrast, if you add a spoon of sand to another glass of water, the sand doesn't melt and the water level increases. What is the difference between the two cases?
A: The 'melting' of crystal-like salt/sugar in water begins with the breaking of the bonds between the molecules/ions of the crystalline substance. With that they get separated into individual molecules (e.g.sugar) or ions (e.g. salt). There is a lot gap between water molecules (that's why it flows) and these salt/sugar ions/molecules get into these gaps and that's why the water level doesn't increase.
Along with this, you can make one more observation. As you keep adding more sugar/salt to the water it keeps melting and the water level stays the same. After a while it gets 'saturated' and it can't take any more salt/sugar, how much ever you stir it! Why? All the gaps between the water molecules are now taken up by the additional salt/sugar and there are no more gaps left. House full! That's when any extra salt/sugar you add will not dissolve in the water and instead will go to the bottom and settle there and now the water level will obviously increase!
Q: In an oil lamp, how does the oil travel upwards towards the burning tip of the wick, against gravity?
A: First, the wick is made of cotton, with tiny air pockets between the fibre cells of cotton. When you wet the wick with oil, it takes the place of the air in those pockets. As the wick burns, it 'consumes' those tiny globules of oil, thus creating tiny vaccums. So, oil in the pot moves into those pockets of vacum, independent of or 'defying' gravity, if you wish.
And more to come....
Best regards,
K. Nagarajan
Bangalore/Bengaluru
Email: knr_sh@yahoo.com